Which UUID version?
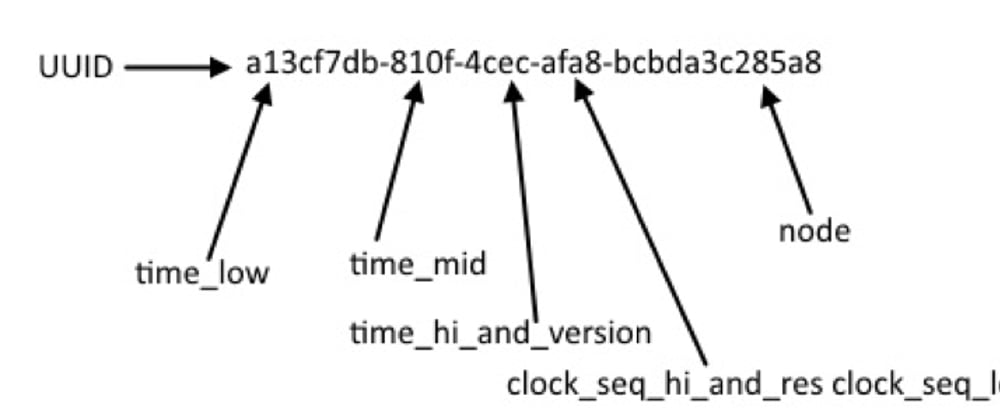
Universally Unique IDentifiers versions are defined by the RFC4122.
They are 5 different versions that have different implementations to generate Unique Identifiers.
v1 TimeUses the CPU clock cycle to calculate a unique ID | v2 MACUses the CPU clock cycle and MAC address to generate a unique ID. | v3 MD5Uses a namespace value to salt the MD5 Hash (128 bits). | v4 RandomUses Pseudo-random numbers to generate a unique ID. | v5 SHA-1Uses a namespace value to salt the SHA-1 Hash (160 bits). |
API
Generally, a UUID library will expose all 5 versions and a few helper functions.
- Version: Provides UUID RFC version
- Parse: Convert UUID string to array of bytes
- Stringify: Convert array of bytes to UUID string
- Validate: Check if UUID is valid
- Nil: All bits are set to
0- 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
Ranking
Uniquenessv1 👊 v2 👊 v4v4 Randomv1 and v2 are similar, but the cpu cycle is predictable. | Hashingv3 👊 v5v5 SHA-1v5 SHA-1 has a stronger encryption than v3 MD5. |
Protectedv2 👊 v1 👊 v4 👊 v3 👊 v5v5 SHA-1v1 and v2 are similar, but the MAC address can make your system less secure. | Overallv1 👊 v2 👊 v3 👊 v5 👊 v4v4 Randomv4 is generally the best option in most use cases. |
